The benefits of magnesium on the body
Magnesium is a mineral salt essential for the proper functioning of the body. It is involved in many cellular processes to keep us healthy. Therefore, a magnesium deficiency can cause several symptoms and clearly decrease your quality of life. Fortunately, this mineral is available in many of the foods that we consume and it is also available as a dietary supplement. Do you want to know more about how to get the most from magnesium? In this article, discover the benefits of magnesium for men and all you need to know about this mineral.
Do you know what magnesium is, this essential mineral?
Magnesium is one of the molecules essential for the functioning of the human organism. In the biological classification, it is said to be a macroelement. In other words, it is normally found more than 5 grams in the body of a 70 kg man . It works in concert with minerals like sodium, calcium and potassium.
Its essential role for our good health
Magnesium is a very important mineral, because it participates in more than 300 biochemical reactions which are essential for the production of energy . In addition, almost half of the body’s magnesium is found in bones and teeth. It is therefore essential in the formation of normal bones, healthy teeth and their maintenance.
The rest of the magnesium is found in muscle, liver and soft tissue. It is therefore an important molecule in muscle reactions. For example, it promotes relaxation of muscle fibers after contraction .
Needs not covered by our diet
Like all essential nutrients, the body’s supply of magnesium must reach a certain threshold to be of benefit. Even with a varied and balanced diet, our body can be in deficit and fall victim to dietary deficiencies. For adults and children, the recommended daily intake is 6 mg of magnesium per pound of weight. In other words:
- A 70 kg man should consume 420 mg per day;
- A 60 kg woman should consume 360 mg per day;
- A 30-kilogram child should consume 180 mg per day.
Magnesium requirements can increase considerably during times of stress , especially as the mineral is eliminated by the kidneys. For example, we ask to increase the recommended daily allowances for growing adolescents, pregnant women and breastfeeding women. 25 mg, 40 mg and 30 mg per day must be added respectively in each of the above cases.
However, these recommended amounts never seem to be fully covered through diet. According to the SU.VI.MAX study, more than 7 out of 10 French people have insufficient magnesium intake . Several reasons explain this deficit. The needs of the body are increasing with our modern lifestyle which is more and more hectic and intense. Consumption of whole grains is decreasing, to the detriment of refined grain products and processed foods that have lower vitamin and mineral content. Foods also lose part of their magnesium during preparation (25% during cooking and 40% if there is draining). Fertilizers used in agriculture contain phosphate which limits the absorption of magnesium .
In addition, magnesium is water soluble. The body therefore eliminates it fairly quickly, even though it is not able to secrete it itself. The elimination of magnesium also increases with intense sports activity, heavy sweating and stressful or extreme conditions (temperature for example) which require a high consumption of magnesium by the cardiovascular system.

Magnesium Taurine B6
- check Latest generation Magnesium Complex: triple synergistic action
- check Unmatched bioavailability, very high concentration and absence of laxative effects
- check 2/3 of the Daily Allowance or 240mg of Magnesium element
The different types of magnesium
Magnesium comes in different forms, as it does with other minerals. The most common are:
- Magnesium bisglycinate;
- Magnesium malate;
- Magnesium taurinate
- Magnesium oxide;
- Magnesium chloride;
- Magnesium citrate;
- Magnesium aspartate;
- Magnesium sulfate;
- Magnesium glycerophosphate;
- Marine magnesium.
The bioavailability of different forms of magnesium
The bioavailability of magnesium varies from one form to another. That is to say that depending on the type of magnesium you consume, only a given proportion will be well absorbed and will have a real impact on your body. The higher this proportion, the better.
Magnesium bisglycinate:
It is a form in which magnesium is combined with glycine. The latter is a non-essential amino acid, made by the body, but necessary for its proper functioning. This type of magnesium has good bioavailability , close to that of organic salts. In addition, the consumption of magnesium bisglycinate does not seem to have any negative effects on human health.
Magnesium malate:
Magnesium malate is the magnesium salt of malic acid. It is used in the composition of certain food supplements thanks to its high bioavailability. Malate also respects the sensitivity of the intestinal wall better. It seems to have a protective action on the kidneys and facilitate colon cleansing. However, there are no conclusive studies on the properties of magnesium malate. There is no concrete evidence on its effectiveness or the absence of side effects.
Magnesium taurinate:
It combines magnesium with taurine which is well assimilated by the intestine and cells. This association confers a very high bioavailability to this form of magnesium but its magnesium concentration remains very low with only 6%.
Magnesium oxide:
It is one of the cheapest salts you will find with a fairly high magnesium content. Unfortunately, its bioavailability is very low. Doses should be divided (maximum 50 mg per dose) to ensure minimum absorption. Beyond that, magnesium is less assimilated and there is a high risk of laxative effect. Magnesium hydroxide has the same characteristics.
Magnesium chloride:
Magnesium chloride has good bioavailability. Many people claim to use it successfully in treating infections, although its effectiveness in this regard has not been well researched. It is also a compound that can have a laxative effect.
In addition, the sodium chloride it contains is an acidifying element . Consuming high doses of magnesium chloride (in addition to the many acidifying foods we consume) can be harmful to health. Older people are more prone to these disorders because their buffer systems work less well. However, the consumption of this salt is indicated in people whose stomachs have difficulty producing hydrochloric acid and in certain conditions involving low levels of chloremia and magnesium (Gitelman syndrome for example).
Magnesium citrate:
Magnesium citrate also has good bioavailability like magnesium bisglycinate and magnesium oxide. Indeed, citric acid is an organic acid having a low molecular weight and it stimulates the absorption of magnesium by improving its solubility. Magnesium citrate is well tolerated by the body, although in high doses it may be responsible for a slight laxative effect in some people .
Magnesium aspartate:
Magnesium aspartate is a form of magnesium that offers even greater bioavailability than oxide and citrate. Clinical studies carried out in the 1960s showed that the combination of magnesium and potassium aspartates acts positively on fatigue and decreases muscle hyperexcitability. On the other hand, Magnesium aspartate is not commonly used because, like glutamate, it is a neuro-exciter . Its action can therefore have a negative impact on nerve cells.
Magnesium sulfate:
Magnesium sulfate is generally used for intravenous formulations, but not for oral intake. It has the particularity of being absorbed by the skin and it is found in certain bath salts.
Magnesium glycerophosphate:
Magnesium glycerophosphate is a salt which has the advantage of being low laxative and soluble in fats. It is therefore fairly well tolerated by the body. But the problem here is the phosphate in this salt which is added to the phosphorus consumed in the diet as well as to the phosphate additives. An excess of phosphate would promote the development of metabolic diseases, especially when you have a history of kidney problems . It is therefore a molecule to be used with caution in the event of renal pathologies and if you consume too much food rich in phosphate. These are mainly foods rich in additives.
Marine magnesium:
Finally, marine magnesium is obtained after the evaporation of sea water. It is a mixture of inorganic salts (oxide, hydroxide, sulfate and chloride) with very variable contents. Marine magnesium has fairly low bioavailability for the human body and may have laxative effects. Often associated with other molecules such as vitamin B6, to compensate for its poor assimilation, it can provide a little extra energy.

The effects of magnesium on the body
Magnesium is an essential mineral because it is essential for the proper functioning of the body, which cannot secrete it on its own. It plays a beneficial role on health at various levels, whether it is on the nervous system, muscles, bones or even teeth for example.
The role of magnesium on the nervous system
Magnesium is a key element in maintaining good physical and mental health. Thanks to its antagonistic action to that of calcium, it has an essential role in the good functioning of the nervous system .
When nerve fibers are excited by calcium ions, magnesium inhibits their action to stabilize the membrane. It is therefore involved in the regulation of nervous activity. Therefore, a magnesium deficiency can lead to imbalance and over-arousal of the nervous system.
An aid to muscle function
In the muscles, magnesium is recognized for its muscle relaxant properties . It plays a key role in muscle contraction and relaxation. It also participates in the production and release of energy therefore helps to maintain normal muscle function.
For the athlete, the regular intake of magnesium improves endurance and reduces the risk of muscle cramps, spasms and tetany. After a workout, the magnesium is used by the muscles to relax again. It is therefore a particularly important molecule if you have to make great physical efforts. Bringing enough magnesium to your body will also help fill the electrolyte losses due to sweating. It therefore contributes to your well-being even if you have an intense daily life.
Can it actually reduce fatigue?
It is not a myth that magnesium helps reduce fatigue. This molecule is necessary for the production and management of energy reserves at the cellular level . After intense physical exercise or when faced with unusual elements such as a high temperature, toxins or even a mental problem, magnesium needs can quickly increase. And when the needs are not met, the muscles slow down, causing fatigue with the slightest effort. In this case, a magnesium cure will allow you to get back into shape fairly quickly.
Is it the same in case of nervous fatigue? Yes. The role of magnesium previously presented is proof of this. Nervous fatigue results in low morale, irritability or even difficulty in staying focused. Magnesium supplementation can provide relief by regulating and optimizing the functioning of the nervous system.
However, it should be noted that not all fatigue will be corrected by a supply of magnesium . An unbalanced diet, too much work or excessive sedentary lifestyle are other factors responsible for fatigue that should be considered if you are exhausted all the time. Chronic fatigue can also be a symptom of an illness. When this persists, it is therefore essential to consult your doctor to be better oriented on the tailor-made solutions to adopt.
Is it effective in case of stress?
Magnesium deficiency can be the cause of a feeling of physical and mental stress . The risk is even higher for those who for genetic reasons badly assimilate magnesium.
Even when stress is not due to a lack of magnesium, it causes too much norepinephrine to be secreted. This neurotransmitter sends a signal that makes the victim overly vigilant and hypertensive. The muscle contractions that occur involve an influx of calcium into the cells. Calcium molecules push magnesium out of cells. And the latter that escapes will go into the blood and then be eliminated by the kidneys. This loss will make the body even more vulnerable to stress.
So it’s a vicious cycle that it’s important to break out of with a magnesium supplement. It decreases the secretions of stress hormones as well as the symptoms associated with them . In summary, magnesium reduces vulnerability to stress in humans. In order to reduce the damaging effects of stress on the body, adaptogenic plants like Rhodiola rosea help protect cells from physical stress and support emotional balance.
Magnesium helps maintain good bones and teeth
Like calcium, magnesium is also necessary for healthy and strong bones. Its impact on bone metabolism is important because it is involved in the structure of the hydroxyapatite crystal. During bone building, magnesium is essential for transporting calcium molecules and it helps regulate their content in the bones.
It is also involved in the activation of enzymes that metabolize vitamin D. Magnesium thus ensures the preservation of bone structure and at the same time the growth of teeth and bones. With age, a magnesium deficiency is therefore a risk factor for osteoporosis. There are a few studies that show an increase in bone density after magnesium supplementation.
How to recognize a magnesium deficiency?
Sometimes the body is severely lacking in magnesium. Unfortunately, it is not possible to identify this lack through a classic blood test, because only 1% of the body’s total magnesium is present in the blood. Apart from thorough clinical examinations, there are still some signs that can alert you . A low intake of magnesium can have the following consequences on your health:
- Anxiety, stress and sometimes even depression;
- Physiological discomfort such as muscle cramps, spasms, insomnia or sleep disturbances, osteoporosis, eyelid tremor…
In addition, certain categories of people are at risk. This is the case, for example, of women who are particularly affected by magnesium deficiency due to losses during menstruation.
How to fill up with magnesium?
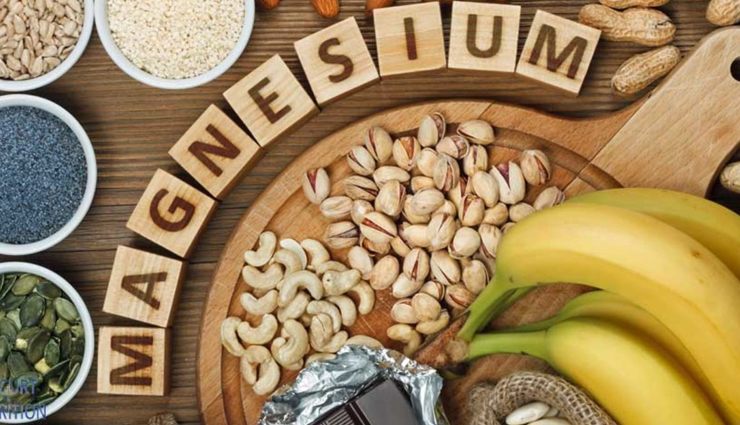
Magnesium is naturally found in many of the foods we eat. This is particularly the case of whole grains such as rice, buckwheat, and quinoa . We speak of a whole grain because the precious mineral is found in the bran, the outer shell of the seed. When bleached and refined, grains become low in magnesium because the husk has been removed.
Vegetables that have dark green leaves are also very rich in minerals and trace elements, including magnesium. It is contained in the center of the chlorophyll molecule. It is also found in oilseeds (almonds, walnuts), fruits (bananas, figs, kiwis, prunes, etc.), legumes (lentils, beans, chickpeas, etc.).
Dark chocolate and certain mineral waters are also sources of magnesium.
With all the diversity of foods that contain it, in normal times and in the absence of stressful situations, a balanced diet should cover the daily magnesium requirements. Here are some figures on the magnesium content of various foods:
- 300 mg in 100 g of periwinkles;
- 285 mg in 100 g of soy flour;
- 270 mg in 150 g of flageolet beans and green beans;
- 106 mg in 100 g of whole dry rice;
- 250 mg in 100 g of cashew nuts;
- 46 mg in 100 g of spinach;
- 255 mg in 100 g of almonds;
- 32 mg in 100 g of cooked lentils;
- 59 mg in a banana;
- Between 35 to 87 mg in 30g of dark chocolate…

With these foods, you can now create healthy, complete menus to give your body the amount of magnesium it really needs every day.
But, even if you have a balanced diet, it can happen that the need for magnesium is not sufficiently covered.. Remember: athletes and people who have an intense daily life or are under stress, as well as women who breastfeed for example, have greater needs. In this case, it then becomes essential to use food supplements in the form of capsules and to make a magnesium cure.
You can do a one-month trial and see any changes (reduction in cramps, tremors, fatigue, etc.). When there is no improvement, it means that magnesium intake is not what you need. Otherwise, when you notice interesting results, continue taking, but for a short period (2 months maximum) and resume after a one-month break. This is to prevent the body from getting used to an excessive intake of magnesium and stop fixing it.
The action coupled with taurine and vitamin B6
Magnesium supplement formulas are designed for easy absorption by the body. Alone, it is not always well assimilated and can be responsible for digestive disorders . Food supplements can therefore contain vitamin B6 so that consumers can enjoy the benefits of magnesium without the side effects. Vitamin B6 also facilitates the entry of magnesium into the cell. In addition, it participates in the regulation of hormonal activity for better functioning of the body. It is involved in the synthesis of cysteine and in the metabolism of homocysteine.
The formation of red blood cells also involves vitamin B6 . Its presence contributes to the proper functioning of the nervous system and optimizes its psychological functions. Finally, it participates in the normal functioning of the immune system and plays an important role in the metabolism of proteins and glycogen.
In some food supplements, in addition to vitamin B6, magnesium is combined with taurine. The latter is an amino acid well recognized by the cells of the body. It improves the assimilation of magnesium, particularly magnesium bisglycinate. It therefore helps fix magnesium molecules in cells . This is important when you remember that 98% of the body’s magnesium is found in cells.
Therefore, a food supplement with a magnesium – taurine – vitamin B6 formula is more effective for having a normal energy metabolism and suffering less from fatigue.
You can probably imagine it: not all commercially available solutions are the same and your choice must take several parameters into account. Here are the most important criteria to consider.
Types of magnesium
As part of a supplement, the choice of form is essential, it is necessary to check the concentration and the bioavailability if one has an impact on the body. The bioavailability of magnesium can vary greatly from one form to another so depending on the type of magnesium chosen, only a given proportion will be absorbed and will have a real impact on the body.
The other nutrients that accompany magnesium
As we have seen previously, other nutrients can accompany magnesium and they are also very useful to the body. Vitamin B6 for example, like other B vitamins, is essential in several reactions involving magnesium. It is therefore interesting to refer you to a vitamin B complex when you have to choose a magnesium supplement . Other molecules like taurine are also beneficial.
However, avoid formulas that have additives like titanium dioxide. It decreases the capacity of intestinal cells for the absorption of nutrients like iron, zinc and fatty acids. In addition, an INRA study indicates that this additive is potentially carcinogenic. Finally, among the other additives to avoid are carboxymethyl cellulose, parabens, microcrystalline cellulose, magnesium stearate and sodium benzoate.
In general, choose a brand that selects top quality products and does not compromise on quality. At Nutripure, we are committed to selecting the best raw materials and to excluding all types of chemical additives, flavorings or solvents that may be dangerous for your health.
Avoid laxative formulas
There are many formulas of magnesium that act as laxatives. To supplement your food intake, these formulas are not the right choice. When choosing, don’t turn to magnesium citrate. It is certainly well absorbed, but it is generally prescribed for acute constipation. In general, avoid inorganic magnesium salts.
The indications on the labels
You always have to read the labels of the products you buy, right? It’s all about recognizing quality dietary supplements, but what to really watch out for when it comes to magnesium? Some labels indicate a composition of 300 mg of magnesium per capsule or tablet, sometimes more. This can be an indicator of the poor quality of the product, as this rate is too high, especially if second and third generation carriers were used. A good quality product requires at least two tablets, if not more, to provide 300 mg of magnesium.
The format and the price
Third generation food supplements are often packaged in pill boxes of 60 to 180 tablets or capsules . These are formats that you can take over one and two months and are sold between 15 and 25 euros depending on the manufacturer.
Our opinion on magnesium bisglycinate
Still called magnesium glycinate, magnesium bisglycinate combines a magnesium atom and two glycine molecules. It is a food supplement very appreciated for its corrective action of the deficiency in magnesium. It thus helps relieve people who suffer from symptoms such as anxiety, sleep problems, migraine, fibromyalgia, tremors …
It is the best form of magnesium as a dietary supplement on the market. She receives a lot of positive reviews from users. One of the main reasons is its high bioavailability. In other words, its absorption by the body is excellent.
Many forms of magnesium absorb very poorly once consumed. For example, magnesium oxide, the most common form, has an absorption rate of 4%. That is, for every 100 mg of magnesium consumed, you will actually only benefit from 4 mg. The rest of the magnesium draws water into the intestine and is eliminated through the stool.
With magnesium bisglycinate, two molecules of glycine are already bound to magnesium. It can then fix very little water, because the wisteria occupies the place where water would normally bind. In addition, glycine helps lower the pH in the small intestine . This has the effect of improving the absorption of the molecule. It should be noted that the consumption of glycine is also beneficial for health. It is an amino acid that helps the body to relax, to better secrete growth hormone and to really get the benefit of sleep.
Another reason why Magnesium Bisglycinate is by far the best form is that it is very gentle on the stomach and the entire digestive tract . Many consumers claim to be able to take higher doses because they can tolerate it much better. Side effects are also much less present.
Dosage and dosage
When you decide yourself to do a magnesium cure, you must ensure an improvement (improvement of sleep or disappearance of cramps for example) after consumption of a maximum of one month. And when it doesn’t, you should see your doctor. If after a daily intake of 300 mg of magnesium (adults) you feel better after a month, it is advisable to halve the dose and rely on a balanced diet for the remainder of the dose you have. need.
In addition to the intake through food, it is recommended not to exceed the following doses in addition:
- 65 mg per day for children between 1 and 3 years old ;
- 110 mg per day for children between 4 and 8 years old ;
- 280 mg per day for children between 9 and 12 years old ;
- 350 mg per day from 13 years and over .
These doses correspond to the maximum amounts that can be consumed as a supplement, in addition to food. These are the daily dosages from which magnesium supplements have caused a laxative effect in some people in a few studies. Other research still suggests higher dosages, going up to 1200 mg per day without causing diarrhea in participants. Note that the magnesium consumed through food does not cause diarrhea.
The dosage of the magnesium supplement may also depend on the condition you are suffering from . For preventive purposes, before exams or a great moment of stress for example, an intake of 100 mg per day is sufficient for a period of 1 to 3 months. But, in a curative protocol, when the signs of the deficiency are already present, the supplementation can go to 300 mg per day for an adult over a period of 1 to 2 months.
When the daily doses are greater than 100 or 200 mg, it is advisable to favor several intakes during the day for better assimilation .
It is also beneficial to provide magnesium in the presence of other vitamins of the BCDE group which participate in 300 biochemical reactions providing energy. With this in mind, Nutripure has integrated one third of the recommended daily intake of magnesium in multivitamins and two thirds in magnesium in order to smooth the intake during the day and promote the synergy of the elements. This also allows the dosage to be adjusted as needed, so you can increase magnesium intake without the risk of zinc overdose, unlike formulas with ZMB which involves zinc.

When to take magnesium?
Magnesium as a food supplement is indicated to fill the gaps in the diet which does not cover our needs in magnesium or omega 3 . You can buy it and start treatment if you have signs of a lack of magnesium such as fatigue, anxiety, irritability, low mood, cramps, difficulty concentrating.
The need for magnesium in athletes can increase by 10 to 20% of the recommended daily allowance, depending on the type and intensity of sports training. When this is the case, supplementation is essential to stay in your best shape.
A lack of appetite or a slimming diet can also decrease the dietary intake of magnesium. It will then be necessary to direct you towards supplementation to avoid a significant deficiency and the negative consequences which ensue.
So what time of day is it best to take magnesium supplements? They can be taken at any time of the day , as long as it is easy for you to take them on a regular basis. For some people, it is easier to take the magnesium capsules or tablets in the morning, while others feel more comfortable taking them with dinner or just before going to bed. The most important thing is to set a precise schedule and stick to it to make sure you stick to your daily dose. It is also noted that taking magnesium supplements with food can help avoid some of their side effects .
When you take it can also be influenced by the medication you are taking. This is especially the case when you have to take your supplements alongside certain medications such as antibiotics. However, keep in mind that the benefits of magnesium supplementation will only be effective with long term use.
Contraindications and side effects of magnesium supplements
Magnesium should be taken at least two hours before or after taking a high dose of calcium, because the latter interferes with the absorption of magnesium by the body.
Magnesium may also be contraindicated while you are on treatment with certain medications such as diuretics, tetracyclines, or aminoglycosides. This is also the case with certain drugs for the heart such as quinidine and digitalis, anticancer drugs such as cisplatin, bisphosphonates for the treatment of osteoporosis … These are drugs or supplements that have scientifically proven interactions with magnesium. The best thing to do when you have ongoing treatment is to consult your doctor or pharmacist to be sure that you are in no danger.
The majority of people who consume magnesium supplements do not experience side effects. But in some cases, for various reasons, you may experience bloating, upset stomach, and intestinal issues like diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. However, it is the consumption of large doses of supplements that often leads to these consequences. Additionally, people with kidney problems are more likely to experience side effects from consuming dietary supplements rich in magnesium.
Excessive doses can have more serious side effects: a change in heart rate, too low blood pressure, mental confusion, breathing problems…
Although dietary supplements are generally considered safe, it is important to seek the advice of a healthcare practitioner before taking them. The following people are particularly affected:
- Victims of kidney failure;
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women;
- People with bleeding disorders;
- Victims of heart problems…
What to remember about magnesium? It is a mineral essential for the proper functioning of the body. Unfortunately, human cells cannot synthesize it for their own use. Magnesium deficiency can be the source of several more or less serious ailments such as fatigue, stress, anxiety disorders and cramps. It is therefore necessary to regularly consume foods that have optimal levels of magnesium.
When the diet is not rich enough in magnesium, or when you need more, supplements are very effective in preventing or correcting deficiencies . To make your choice, you must prioritize the bioavailability of the chosen formula. Prefer formulas that offer combinations with other interesting molecules such as vitamin B6 and taurine. They improve the assimilation of the mineral and have other beneficial virtues for man.
Also avoid formulations that have been concocted to have a laxative effect. Do not hesitate to also seek the advice of your doctor if you are already under medication, or a nutritionist for advice tailored to your situation or your physiological state. Finally, choose a reliable supplier to have quality products.